Climate Action as a Blueprint for a Healthier World
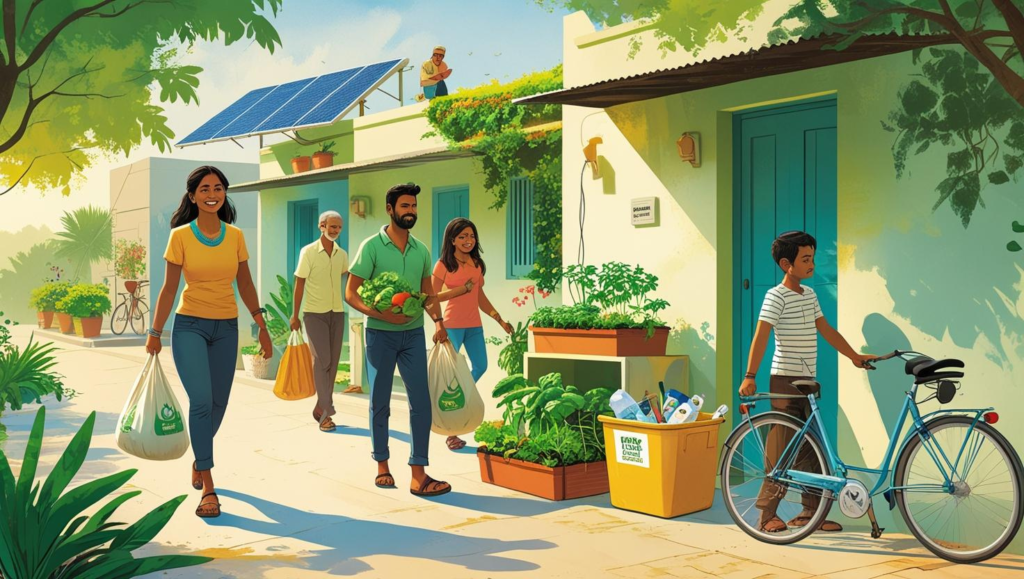
We talk about climate change all the time, as if it is something we have to “fight” or “limit,” trying to lower emissions to avoid exceeding a now-mythical 1.5°C global temperature increase. After researching several articles on sustainability, I’ve come to realize that climate action is much more than just simple damage control.Let’s dive in for what it is, a big opportunity to change the society in a way that is beneficial for everyone i.e. with clean air, better health, stronger communities and stable economic flow.Let’s explore how climate resources touch each fabric of our lives, and how commodifying it in full can unleash a good future for all. Clean Energy: A Catalyst for Positive Change The shift towards renewable energy is more than just a temporary technical fix. It’s a movement that redefines our economy, our infrastructure, and even our public health. Solar, wind, and hydro power are no longer niche or expensive. In many parts of the world, these energy sources are now accessible and affordable. Affordability is now opening new doors for today’s generation due to various reasons such as: Economic Growth: Now securing a job in the renewable energy domain is faster than traditional energy jobs, which offer a new livelihood to both urban and rural communities. Energy Stability: As countries are relying less on imported fuels, hence become less and less vulnerable to global market shocks and supply chain disruptions occurring from time to time. Health Benefits: Reducing the use of fossil fuels and shifting to clean energy resources directly improves air quality, reducing asthma and heart disease—especially in densely populated areas. Cross-Sector Applications: Renewable power has gained application beyond just homes, Now it fuels electric transport, powers industrial machinery, and helps generate clean fuels like green hydrogen. Also Battery storage, smart grids, and policy support are ensuring that this transition is not only clean but also reliable. Nature: A Powerful Partner in Climate Solutions You might think of different causes for this disruption, but Nature itself is the victim and solution for climate change. Following are a few of the ways of restoring and protecting natural ecosystems. This helps in absorbing emissions while strengthening resilience. Forests & Agriculture: Forest conservation and a shift towards sustainable farming is one of the most effective methods to preserve biodiversity while sequestering carbon. Meanwhile, a shift into this approach will in turn help in stabilizing the local weather patterns. Composting, agroforestry, and reduced tilling are beneficial for the boost in both yields and climate resilience. Coastal Defense: Coastal flooding and erosion can be controlled by wetlands, mangroves, and seagrass beds as they absorb enormous amounts of carbon and act as buffers. Smarter Waste Use: Open burning of food and other waste as well as poor waste management does contribute heavily in increasing methane emissions. Community composting and circular economy models can make a significant dent in both emissions and waste volume. What’s key is that these above listed strategies don’t just help the climate but also improves soil health, creates local jobs, and reduces disaster risks. Innovation, Policy & Finance: The Enablers of Change In today’s world, despite having access to all the technologies and nature-based tools, their real-world adaptation depends on a mix of supportive policies, forward-thinking leadership, and accessible finance. Efficiency First: Switching to renewables and making it more affordable is possible by using less energy through better buildings, appliances, and transit. Carbon Markets: Properly regulated carbon credit systems offer financial incentives for companies and communities to invest in low-carbon solutions. Government Role: National and local governments are crucial in scaling climate solutions by implementing policies like subsidies, tax breaks, climate legislation, and public infrastructure investments. These actions create an environment that encourages the adoption of sustainable practices and technologies. As India is a developing nation, the Indian market is now paving its way globally and is becoming a hub for these emerging national carbon markets. Hence the right support from the government and the right policy mix can turn these climate ambitions into measurable outcomes. Resilience Built In: Climate Solutions That Withstand the Test of Time As per the available data many actions have been taken to reduce emissions by different organisations, government, individuals as well and help us prepare for climate-related shocks. For instance:Solar renewable energy is integrated in hospitals to keep the life saving machines running during power cuts caused by extreme weather. New farming techniques like vertical farming are climate-resilient farming methods which protect food supplies during heatwaves or droughts, reducing water consumption, and year-round crop production. For the vulnerable community decentralization of water and energy systems will help in building independence amongst them.Mitigation and adaptation are two terms that are now no longer considered separate, because in today’s fast growing world these two terms lead to a common goal. Everyone Has a Stake in This As per today’s need for sustainable development, this should go hand in hand with a common goal and not the responsibility of any one particular group. Thus, let’s take a glance around this sustainable development as a collective journey involving:Governments- responsible for setting the framework and goals. Private companies- driving innovation and investment. Communities and individuals- ensuring ground-level engagement and accountability.Aligning all these elements will not only avoid this climate crisis but will in turn alleviate us as a society to actively build something better for the upcoming generations. So What’s Next? As climate action is evolving, a new vision for development should emerge as it’s no longer just about survival, it’s about creating a system that works better for everyone. Access to cleaner energy, smarter farming, healthier cities, simultaneously restoring the ecosystem should be considered as the new achievements that need to be unlocked!Now the real question is: What role will you play in restoring nature?Have you seen examples of climate solutions working well in your neighborhood or industry? So what part of a project are you involved in that’s making a real impact? Let’s connect via comments, share insights, and push this movement
Climate Action as a Blueprint for a Healthier World Read More »